What’s the Difference Between an ECU, ECM, TCM, and PCM?
Your vehicle is a complex array of mechanical and electrical components working together while you drive. Computer modules control nearly all mechanical parts of modern vehicles (engine, drivetrain, transmission, etc.). Control modules monitor and dictate different values, allowing the car to run correctly. Your vehicle contains many control modules, but when it comes to the engine and drivetrain there are three common types; the ECM, TCM, and PCM.
It can be confusing to decode these terms and understand what they mean and ultimately, know what’s wrong with your car. Let’s go over what these acronyms stand for, and what they do!
History of Vehicle Engine Management
Before we get into what all those acronyms stand for, let’s look at the history of engine management. Before the rise of computerized control modules, engine functions were set and controlled mechanically or pneumatically.
Ignition timing (spark), for example, was controlled by a distributor, connected directly to the engine with a distributor shaft. The rotation of the engine dictated when the spark plugs would ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. You might also imagine an old muscle car with a carburetor that needs to be adjusted by hand so the engine runs properly. These older technologies worked well but lacked accuracy and could be finicky.
In the late 1960s, the first electrical engine management systems were developed for passenger vehicles. By the late ‘70s and early ‘80s, mechanical systems like carburetors and distributors began to fade out in favor of electronic fuel injection and coil-on-plug ignition, among other things (carburetors and distributors were installed until 1990 and the early 2000s respectively).
Computerized engine management came along with these changes in technology.
Advances in engine management led to better performance, reliability, and fuel economy (once the kinks in the early systems were worked out).
Nowadays, cars and trucks are fully computerized, from the engine and transmission to the dash, interior, and navigation systems.
What Do ECM and ECU Stand For?
ECM stands for Engine Control Module, and ECU is short for Engine Control Unit. These two acronyms represent the same component and are used interchangeably.
What is an ECM (or ECU), and What Does It Do?
The ECM/ECU is a module that oversees all engine functions and allows the vehicle to operate properly. Information is sent to the module from sensors throughout the vehicle, including oxygen sensors, crank, and camshaft position sensors, mass air flow (MAF) and manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensors, coolant temperature sensors, throttle position sensors, and more.
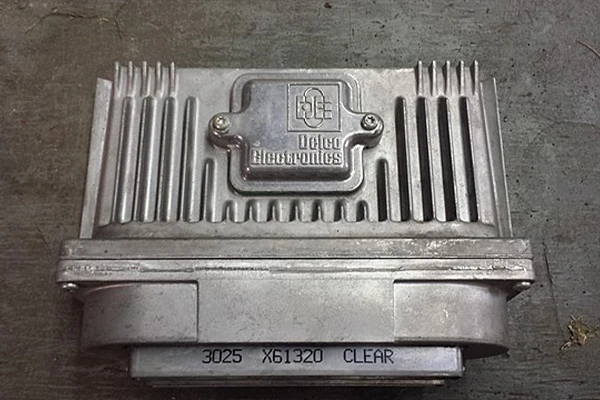

The engine can operate smoothly thanks to the ECU actively managing and controlling the engine based on these values. The ECM/ECU controls many operations:
- Idle
- Variable valve timing
- Fuel injection
- Emissions systems
- Cruise control
If the module detects any malfunction, it will alert you with a warning light on the dash and can even put your vehicle into limp mode, which restricts its performance to prevent engine damage.
You may have heard people refer to the engine control module as the “brain” of the car, and given all the functions this computer performs, that’s a pretty accurate description!
What Do TCM and TCU Stand For?
TCM and TCU stand for Transmission Control Module and Transmission Control Unit respectively. These acronyms can be used interchangeably.
What Does the TCU/TCM Do?
The transmission control unit/module oversees the function of automatic and dual-clutch transmissions. This module reads vehicle speed sensors, transmission fluid temperature, throttle position, and more.
The TCU/TCM decides when to change gears to optimize performance, acceleration, and fuel economy. When you drive a car with an automatic transmission, the effortless shifts that always happen at the right time are a direct result of the TCM/TCU.
Vehicles with manual transmissions do not have a transmission control unit/module because the driver is the one making the decisions!
What is a PCM and What Does It Do?
PCM stands for Powertrain Control Module. The PCM is a control unit that performs the TCM/TCU and ECM/ECU functions together. The power train control module controls all aspects of the power train including the engine, transmission, and driveline. The PCM integrates the functions of the ECU and TCU into one, giving control of the entire powertrain to a single module.
Control Modules Are Not Standardized Across Brands
You won’t see a standardized use of these modules across vehicle manufacturers. Some brands may use a PCM while others may use a TCM and ECU combination. Depending on the type of car you own, the associated acronym and module will vary. To make things even more confusing, some manufacturers will use PCM and ECM interchangeably.
Control Module Diagnoses and Repair at Borst Automotive
Electrical issues can be the most difficult to diagnose, especially in modern cars. Many of the tools needed to diagnose control modules are extremely expensive or not available directly to the public. If you suspect issues with your ECM, TCM, or PCM, save the headache and bring your car to a professional.
Borst Automotive is your one-stop for vehicle control module service. Our expert technicians have the skills, experience, and tools needed to diagnose, replace, or reprogram any of the complicated modules in your car and get you back on the road fast. We have four locations in Tucson, Phoenix, and Mesa Arizona. Give us a call or schedule an appointment online today!
Borst Automotive is here to help when you need it. Give us a call, schedule an appointment, or stop in today!
